Macro & Micro Nutrition
One of the first major steps into
developing a nutrition plan we must break it down to the bare minimum of
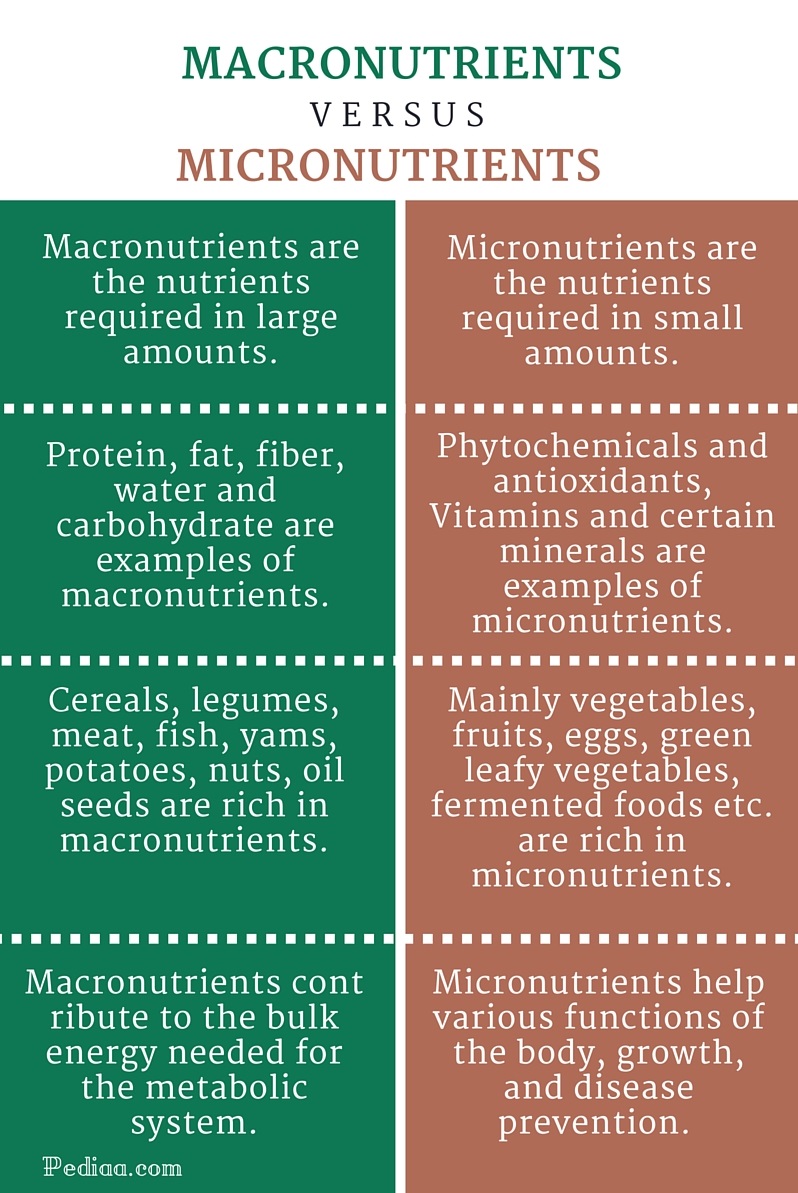
nutrition. The nutrients are classified into six classes, Carbohydrates, Fats,
Protein, Vitamins, Minerals, and Water. (Sizer & Whitney, 2017, p. 7) Out
of the six nutrients four of them are organic which are fat, protein,
carbohydrates, and vitamins. Of the four organic nutrients carbohydrates, fats,
and proteins are energy yielding nutrients, which means that the body can use
the energy that come from these nutrients as Sizer & Whitney (2017)
explains, it’s also noted that protein can yield energy and provide materials
that form structures and working parts of body tissue. The next set of
nutrients that make up a persons body are vitamins and minerals. Vitamins and
minerals act as regulators, “As regulators, the vitamins and minerals assist in
all body processes: digesting food; moving muscles; disposing of wastes;
growing new tissues; healing wounds; obtaining energy from carbohydrates, fats,
and protein; and participating in every other process necessary to maintaining
life.” (Sizer & Whitney, 2017, p. 7). One of the most important nutrients isn’t
consumed enough on a daily basis would have to be water. Water comprises of 75%
body weight in infants to 55% in elderly and is essential for cellular homeostasis
and life. (Popkin, B. M., D’Anci, K. E., &
Rosenberg, I. H., 2010)
Now that the basics of what makes up a nutritional diet have
been laid out now the five characteristics must been discussed. The Adequacy,
which is the dietary characteristics of providing all of the essentials
nutrients, fiber, and energy in amounts sufficient to maintain health and body
weight such as eating food in high iron like legumes, the other characteristic
would be balance which is the dietary characteristic of providing foods of a
number of types in proportion to each other for example consuming diary
products to obtain more calcium where some other food groups would lack calcium
such as beef, the next characteristic would be calorie control which is the
dietary characteristic of controlling energy intake which could control fat
intake, Moderation would be considered
the dietary characteristic of providing constituents within set limits not
excess such as saturated fats, added sugars, and salt; the final factor of a
nutritious diet would be variety which is the dietary characteristic of
providing a wide selection of food, the benefit of having a variety is that
each different meal could be more nutritious. (Sizer & Whitney, 2017, p. 11-12)
Popkin, B. M., D’Anci, K.
E., & Rosenberg, I. H. (2010). Water, Hydration and Health. Nutrition
Reviews, 68(8), 439–458. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-4887.2010.00304.x
Sizer, F. & Whitney, E. (2017). Nutrition:
Concepts and controversies (14th ed.). Mason, OH: Cengage
Learning


Comments
Post a Comment