Connection Between Nutrition & Disease
When deciding on making a lifestyle change one must first analyze the benefits of a well-balanced nutritional plan. The benefits of a well-balanced nutritional plan can affect multiple types of wellness from physical, mental, social, and emotional, etc. According to Sizer & Whitney (2017) the chronic disease such as heart disease, diabetes, some kinds of cancer, dental diseases, and adult bone loss all have a strong connection with poor diet decisions and when looking at those statistics of those diseases most if not all could have been easily prevented with a proper nutrition plan. Once the onset of the disease affects a person other factors come into consideration. Claydon, Austin, & Smith (2016) explains that depression and obesity are highly correlated, with the risk of depression increase as BMI increases, so not only does a person have challenges physically with poor nutrition the same individual faces mental adversities due to poor nutritional choices.
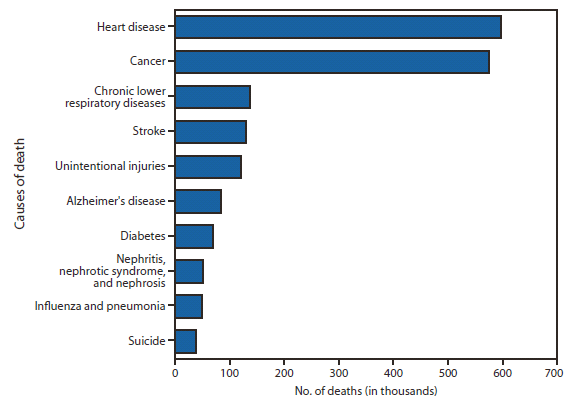
When thinking of the the causes of death the top 10 diseases are as follows stated by Nichols (2017).
When thinking of the the causes of death the top 10 diseases are as follows stated by Nichols (2017).
The top 10 leading causes of death in the U.S.:
- Heart disease
- Cancer (malignant neoplasms)
- Chronic lower respiratory disease
- Accidents (unintentional injuries)
- Stroke (cerebrovascular diseases)
- Alzheimer's disease
- Diabetes
- Influenza and pneumonia
- Kidney disease (nephritis, nephrotic syndrome, and nephrosis)
- Suicide
As we can see when analyzing the chronic diseases heart disease, cancer, and stroke are in the top 5 as leading causes of death which could be combatted with a healthy diet.
In 2017 everyone is more aware of health and wellness, it’s important to note that underweight also increases the risk of death for surgical patients and for anyone fighting diseases. At the same time the risk of having too much body weight could have risks such as chronic diseases (arthritis, breathing problems, cancers, diabetes, heart disease, hypertension, gallbladder, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and stroke), obesity and inflammation, and other risks. Below is attached an image of the effects of malnutrition.
Claydon, E., Austin, A., & Smith, M. (2016). Linking Obesity Prevention and Mental Health Promotion to Address Health Disparities. Community Mental Health Journal, 52(4), 395-398. doi:10.1007/s10597-015-9915-z
Martorell, R. (1999). The nature of child malnutrition and its long-term implications. Food and nutrition Bulletin, 20(3), 288-292.
Martorell, R. (1999). The nature of child malnutrition and its long-term implications. Food and nutrition Bulletin, 20(3), 288-292.
Nichols, H. (2017, February 23). "The top 10 leading causes of death in the United States." Medical News Today. Retrieved from http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/282929.php.
Sizer, F. & Whitney, E. (2017). Nutrition: Concepts and controversies (14th ed.). Mason, OH: Cengage Learning


Comments
Post a Comment